How can we leverage ICTs to address Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)?
Worldwide, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are responsible for more deaths than any other disease. Non-communicable diseases account for approximately 70% of deaths worldwide, of which three-quarters occur in low- or middle-income countries (LMICs). At the same time, digital tools are increasingly being used to provide better and faster healthcare through services that are more empowering and accessible for patients, more efficient for providers and more cost-effective for health systems.
Co-chaired by Dr. Ann Aerts of the Novartis Foundation, and Intel Corporation, the 2018 Digital Health Working Group focused on leveraging digital health to address Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs) through primary health care to improve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) with the vision of generating knowledge on digital health opportunities, best practices and challenges, particularly in low- or middle-income countries (LMICs). The Working Group’s 2018 outcome report aimed to raise awareness and propose practical recommendations and case studies to support governments as they developed strategies to address NCDs.
Setting the Stage
Addressing NCDs to Realize Universal Health Coverage
What are NCDs?
Non-communicable diseases are the leading cause of death and disability globally. Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes and respiratory disease caused 41 million deaths in 2016, accounting for 71% of deaths globally. Unlike communicable diseases (CDs), NCDs are chronic and sometimes lifelong conditions.
Why are NCDs a global challenge?
In many countries, access to health is a persisting challenge: according to the World Bank, in 2018 there was only 0.2 doctor and 1.2 nurses/midwives per 1,000 people in Sub-Saharan Africa (versus 3.5 and 7.6 respectively in the European Union). In addition to combatting acute infectious diseases, more than ¾ of NCD deaths – 31 million – occur in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs); however, only 1% of global health funding is aimed at preventing NCDs.
The Way Forward
Conclusions and Recommendations
-
Properly addressing NCDs is essential to achieve Universal Health Coverage, which is where all people can access the health services they need without suffering financial hardship.
The Working Group outcome report: The Promise of Digital Health: Addressing Non-communicable Diseases to Accelerate Universal Health Coverage in LMICs provides examples from over 30 countries, insights and recommendations for greater sustainability in digital health.
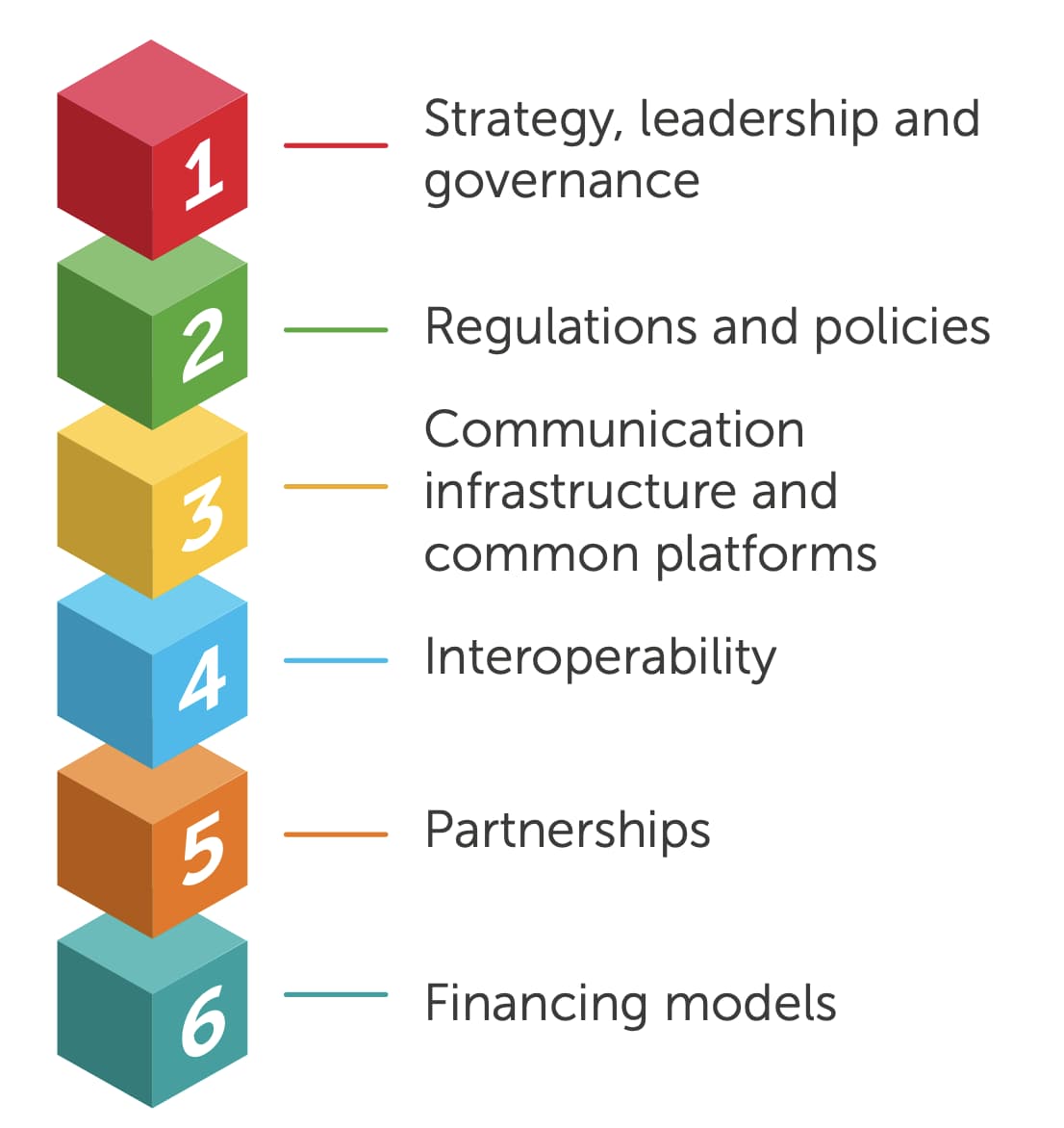
The report identifies six building blocks for sustainable digital health solutions, which can help countries realize the promise of digital health and transform access to appropriate, effective NCD care. Policymakers, donors, private companies and other digital health stakeholders can use the practical lessons, examples and tools described in this report to foster sustainable digital health solutions that address the specific needs of patients with NCDs and help countries achieve universal health coverage more rapidly.
- Define a national health strategy that supports the transformation of NCD management
- Enact strong high-level government leadership
- Align with stakeholders both within and outside the government
- Set up a governance structure
- Stimulate innovation
- Establish a robust monitoring and evaluation framework that draws on existing frameworks such as the WHO’s Guidance on Monitoring & Evaluating Digital Health Interventions
- Invest in training and knowledge sharing
- Create appropriate data-protection and data-quality policies and regulations, thus enabling digital health systems to support UHC
- Approval and safety measures
- Delivery of new healthcare services
- Create awareness of connectivity issues, and make coverage and affordability within mobile/fixed broadband and mobile cellular networks a strategic digital health topic
- Make platform development a strategic topic across sectors
- Define functionalities and use cases for a common health platform
- Establish an information – and application – architecture blueprint and roadmap
- Make interoperability a strategic priority
- Set up a standards and interoperability board
- Create awareness of the importance of interoperability
- Make use of existing interoperability profiles and base standards
- Identify the health needs and the right partners to address them
- Create an environment where partners can meet
- Make sure the structure of the partnership is clear
- Support partners in realizing the benefits of collaborations
- Monitor and evaluate the performance of the partnership
- Assess current financing mechanisms and seek innovative business models for: health IT systems
- Assess current financing mechanisms and seek innovative business models for: digital health solutions
- Assess current financing mechanisms and seek innovative business models for: activating cost-containment measures
- Digital health should be viewed as an essential part of the healthcare system, just as medical equipment or hospital beds are. Realizing the problem involves putting into place the six building blocks presented in this report.
The Working Group Model
Composition and Activities
- Novartis Foundation (Chair)
- Intel (co-chair)
- ITU
- Government of Rwanda
- Government of Ethiopia
- Government of Pakistan
- European Commission
- UN-OHRLLS
- African Commission
- GSMA
- UN Foundation
- Nokia
- KT Corporation
- Global Partnerships Forum
- Microsoft
- Huawei Technologies
- UN Global Pulse
- America Movil
- Inmarsat
- WHO
- World Bank
- PAHO
- Vital Strategies
- The Union
- USAID
- PATH
- Asia eHealth Info Network
- NCD Alliance
- Norad
- Praekelt
- Gates Foundation
- Orange
- Axa
The Broadband Commission Working Group on Digital Health was tasked with identifying countries that have successfully integrated health information systems, ICT infrastructure, and health ICT application, showcasing best practices and tools.
The Promise of Digital Health is the second report of the Working Group, following the publication of Digital Health: A Call for Leadership and Cooperation between ICT and Health.
Fundación Carlos Slim, together with the Novartis Foundation and the Mexican Ministry of Health, held a joint event titled: “Harnessing the power of Digital Health and Big Data to design and implement effective public health policies in Latin America” in Mexico on 24-25 October 2018 to promote the Working group on Digital Health and NCDs report. This event featured the report in Spanish and focused on health issues in Latin America.
Focus Area
Outcome Resources
Co-Chairs
Dr. Ann Aerts
Head, Novartis Foundation
&
Intel Corporation
Broadband Advocacy Targets
SDGs



 Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation 



